
The FDA's (Rockville, MD, www.fda.gov) first approval in the United States of a vaccine for humans against the H5N1 influenza virus marks an important step forward in protecting the public against a pandemic influenza outbreak.

The FDA's (Rockville, MD, www.fda.gov) first approval in the United States of a vaccine for humans against the H5N1 influenza virus marks an important step forward in protecting the public against a pandemic influenza outbreak.
Are the deadlines for your outsourced projects often not met? Are you unsure of the status of your project at any given time? Is the original budget of your study typically exceeded?

Process monitoring ensures that the process performs within the defined acceptable variability that served as the basis for the filed design space.
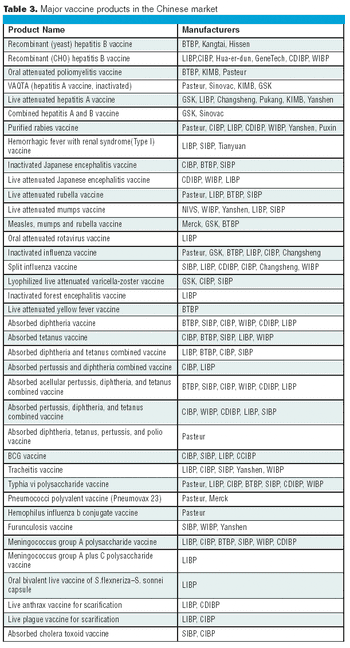
The Chinese vaccine market competition is now transferring from the former price-competition model to a technology- competition model.
Frequently asked questions on implementing and using single-use technologies

Patients receiving palliative care in hospices, hospitals, and other settings can benefit from a subcutaneous injection of morphine with Hylenex recombinant (hyaluronidase human injection).

Cell Therapeutics, Inc. (CTI, Seattle, WA, www.ctiseattle.com), has formed a new spin-off company, Aequus BioPharma, Inc., to develop a novel process to extend the half-life of proteins.

Manufacturing recombinant proteins at industrially relevant levels requires technologies that can engineer stable, high-expressing cell lines rapidly, reproducibly, and with relative ease. Commonly used methods incorporate transfection of mammalian cell lines with plasmid DNA containing the gene of interest. Identifying stable, high-expressing transfectants is normally laborious and time consuming. To improve this process, the ACE System has been developed based on pre-engineered artificial chromosomes with multiple recombination acceptor sites. This system allows targeted integration of single or multiple gene copies and eliminates the need for random integration into native host chromosomes. To illustrate the usefulness of the ACE System in generating stable, high-expressing cell lines, we present several case studies covering CHO cell lines expressing monoclonal antibodies.

The three largest players have accumulated, or are in the process of accumulating, nearly a million liters of capacity between them.
Biopharmaceutical processes typically require a significant investment in equipment-often a substantial obstacle for start-up companies. The risk of drug development failure is often high, further limiting access to the required capital. Flexibility and lower capital outlays are required not only by start-up companies, but also by research organizations with multiple product lines and by companies requiring quick capacity increases. Disposable technologies offer the highest potential for these companies to meet their business requirements. With lower capital requirements and increased flexibility, disposables are an important part of these companies' risk management strategy.

The number of biotechnology-based human therapeutic products in the late-stage pipeline, and the average cost to commercialize a biotech product, have steadily increased. This has required biotech companies to use economic analysis as a tool during process development and for making decisions about process design. Process development efforts now aim to create processes that are economical, as well as optimal and robust.

If a company wants to reduce costs, it should consider outsourcing some manufacturing and analytical testing to low-cost sites.

This article shows how Probabilistic Tolerance Intervals of the form, "We are 99% confident that 99% of the measurements will fall within the calculated tolerance limits" can be used to set acceptance limits using production data that are approximately Normally distributed. If the production measurements are concentrations of residual compounds that are present in very low concentrations, it may be appropriate to set acceptance limits by fitting a Poisson or an Exponential Distribution.

We often assume we know what success looks like for our partner, but we never ask them, or take the time to write it down.

Established, fully validated methodology and SOPs are required prior to initiation of any training activities.

Development reports document process development and support the design of validation experiments, yet in many firms training is not provided nor are expectations established. This article describes how project managers can help scientists master the art of report-writing.
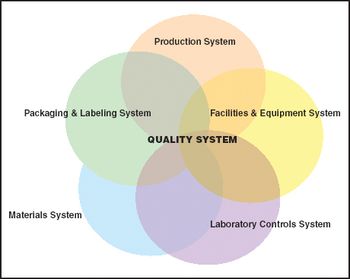
Companies faced with real or threatened FDA sanctions are usually least prepared to react effectively.

Steam traps are part of a steam-in-place system. The current design allots 18 in. of vertical leg for condensate backup. A design with a sensitive bellows has been proven in laboratory tests to need only 6 in. of vertical leg during the 15 min. of 121?C sterilization. Loads of 1 to 27 lb/h are covered by the capability of the new trap, equivalent to required steam for vessels 20 to 40,000 L.
Nothing beats a good dictionary. It can clarify doubts, settle an argument, or prompt exploration into new areas of learning.

Understand your company's requirements, define responsibilities,and manage your team effectively.
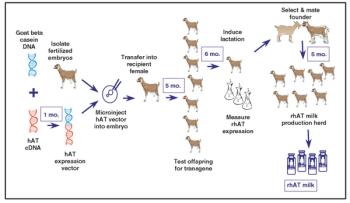
Capital investments in production plants represent a significant portion of the cost of new recombinant drugs

Disposables require less space than conventional equipment, and they can be assembled offsite into complete process trains.

The approvals of two groundbreaking vaccines in the last month is encouraging news. Vaccines have long been undervalued because they haven't been as profitable as other pharmaceuticals. So it's good to see them getting deserved attention that goes beyond fears of flu outbreaks.

"Clinical data is the gold standard" for setting manufacturing specifications, said Patrick Swann, PhD, acting deputy director of the Division of Monoclonal Antibodies at FDA, at a session on specification setting at the AAPS National Biotechnology Conference that was held June 19-21 in Boston.

Several recent approvals highlight progress in developing both prophylactic and therapeutic vaccines.