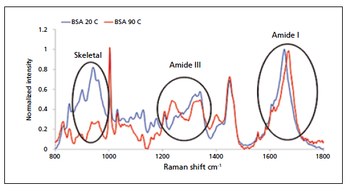
In this article, the author reviews some of the techniques that can yield valuable information on protein stability, focusing specifically on protein aggregation. Emphasis is placed on the enhanced information made available when technologies are used orthogonally, and the alignment of different approaches with specific stages of the biopharmaceutical development workflow.