Gail Sofer
Articles by Gail Sofer


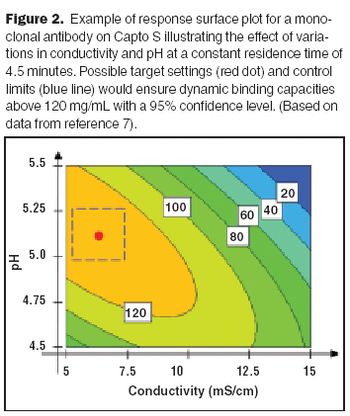
Increased resin stability can extend the number of cleaning cycles that can be performed in situ.

Biopharmaceuticals are perceived as being at risk of transmitting spongiform encephalopathies to patients, although there has never been such an incident. Clearance studies such as the one described in this article (using a TSE model) can validate inactivation and enhance confidence in the safety of therapeutics produced using animal-derived cell culture supplements.

by Gail Sofer, BioReliance

by Gail Sofer, BioReliance

by Gail Sofer, BioReliance

by Gail Sofer, BioReliance

by Gail Sofer, BioReliance, Dorothy C. Lister, and Jeri Ann Boose

by Gail Sofer, BioReliance

by Gail Sofer, BioReliance

by Gail Sofer, BioReliance

by Gail Sofer, BioReliance Dorothy C. Lister, and Jeri Ann Boose Smallest of the microorganisms, viruses depend on other cells ? like those used by biopharmaceutical manufacturers ? for reproduction. And viruses and drug products are idiosyncratic: Both the inactivation process and the product strongly influence the successful outcome. In this conclusion to the virus inactivation series, model ivruses are used to represent single- and double-stranded DNA and RNA viruses, to enable you to reach conclusions about effective inactivation methods for a range of viruses.

by Gail Sofer, BioReliance With West Nile virus in the news, viral inactivation is under public scrutiny. Yet, the culture media, the therapeutic product, and the potential viral contaminants can all affect the inactivation method chosen during production. Viral inactivation techniques ? those tried or used in manufacturing or in final biopharmaceuticals, vaccines, and media products ? have been gathered from recent scientific literature and organized in this article series as an addition to your process development toolbox.

by Gail Sofer, BioReliance The latest installment of our series on recently published methods for inactivating viruses reviews the literature on virus inactivation in plasma and plasma products by chemical treatments, gamma and UV irradiation, and low-pH treatment.

by Anurag S. Rathore, Joseph F. Noferi, and Edward R. Arling from Pharmacia Corporation, and Gail Sofer, Bioreliance; Peter Watler, Amgen, Inc.; and Rhona O'Leary, Genentech, Inc. The trick to process validation, these industry experts argue, is to understand that it is a process that stretches through the whole product life cycle. Some secrets of success: Take a team approach; focus on the timing of the various stages of validation; avoid some common mistakes; and build your documentation as you go.

by Gail Sofer, BioReliance Smallest of the parasites, viruses depend completely on other cells (animal, bacterial, or vegetable) for reproduction ? several hundred viruses infect humans. Viruses can be inactivated by extremes of pH, heat, UV, desiccation, antiseptics, disinfectants, and organic solvents among others. The trick is in finding the right antiviral method for a particular virus ? without harming the biological product of interest. With Part 2 of this literature survey, we look at viral inactivation methods for RBCs and platelets.

by Gail Sofer, BioReliance Viruses present dangers (and therefore challenges) to biopharmaceutical manufacturing processes. The virus inactivation method chosen depends on the virus and its surrounding medium. This survey article, organized by sample type, lists viral inactivation methods published during the past decade. Part 1 presents data for skin and bone and for cells that are not platelets or blood cells.

by Gail Sofer, BioReliance Plasma products have been associated with high levels of risk from viral contamination; therefore, most viral inactivation methods described in the literature during the past ten years have addressed plasma and plasma products. Plasma is the largest group to cover, and Part 3 takes two articles in our series to describe the many methods published. This article covers heat and solvent/detergent inactivation treatments for plasma.
Latest Updated Articles
 VALIDATION: Advances in the Validation of Chromatographic Processes
VALIDATION: Advances in the Validation of Chromatographic ProcessesPublished: February 2nd 2007 | Updated:
 Downstream Processing: Improving Productivity in Downstream Processing
Downstream Processing: Improving Productivity in Downstream ProcessingPublished: November 1st 2006 | Updated:
 Virus Inactivation in the 1990s and into the 21st Century
Virus Inactivation in the 1990s and into the 21st CenturyPublished: April 15th 2003 | Updated:
 Virus Inactivation in the 1990s ? and into the 21st Century: Part 3b, Plasma and Plasma Products (Treatments Other than Heat or Solvent/Detergent)
Virus Inactivation in the 1990s ? and into the 21st Century: Part 3b, Plasma and Plasma Products (Treatments Other than Heat or Solvent/Detergent)Published: October 15th 2002 | Updated:
 Process Validation: How Much to Do and When to Do It
Process Validation: How Much to Do and When to Do ItPublished: October 15th 2002 | Updated:
 Virus Inactivation in the 1990s ? and into the 21st Century Part 3a, Plasma and Plasma Products (Heat and Solvent/Detergent Treatments)
Virus Inactivation in the 1990s ? and into the 21st Century Part 3a, Plasma and Plasma Products (Heat and Solvent/Detergent Treatments)Published: April 15th 2002 | Updated: